
In order to use a NC program not only for just once machining applying a specified value or must work out a value, counting parameter can be used. you can compute or set the value you need by controller when program is running; parameter value can be set through panel. If parameters are assigned, they can assign address specified by variable.
R0=...
to
R249=...
Aggregately 250 counting parameters can be used
R0...R99 – use freely
R100...R249 -pass parameter of machining cycle
If machining cycle is not used, these counting parameters of this part can be used freely.
R0=3.5678 R1=-37.3 R2=2 R3=-7 R4=-45678.1234
You can assign a bigger range using exponential notation :
(10-300...10+300).
Exponential quantity is after EX ; maximum symbolic number : 10 ( including symbol and decimal ) .
EX value range :- 300 to + 300
R0=-0.1EX-5 ; meaning:R0=-0.000 0001
R1=1.874EX8 ;meaning:R1=187 400 000
Notation : There can be more than one assignment statement in a program segment; Also you can assign by computation expression.
Commonality of NC program can be increased by other NC address assignment computing or parameter expression. You can assign any NC address with numerical value, arithmetic expression or R parameter except address N, G and L.
When assigning writes in symbol " = " after address character.
Assignment statement can assign - negative sign.
When assigning coordinate axis address ( running command ) , there must be an undependent program segment .
Example :
N10 G0 X=R2 ;assign X axis
Follow digital operation rule when counting parameter. Operation in former bracket is precedence. In addition, multiplication and division take precedence of addition and subtraction.
1 )、marker is used mark object program segment jumping to, and the jumping function can make program run branch.
2 )、Marker can be selected freely, but it must be composed with one letter or number and the first two symbol must be letter or underline.
3 )、Colon must be after marker of object program segment jumping to. The marker is in the front of program segment. If program has paragraph number, marker follows paragraph number to heel.
4 )、Marker can not have other meaning in a program segment.
N10 MARKE1:G1 X20 ;MARKE1 is marker, object program segment jumping to ...
TR789:G0 X10 Z20 ;TR789 is marker, object program segment jumping to has no paragraph number
When NC program is running, program segment is executed according to sequence of writing in.
When program is running, change executing sequence by inserting skip instruction .
Jumping aim only can be program segment with marker. The program segment must lie in this program.
Absolute skip instruction must occupy an undependent program segment.
GOTOF Lable ;Forwards jumping
GOTOB Lable ;Backwards jumping
AWL illustration
GOTOF Forwards jumping
GOTOB Backwards jumping
Lable Selected marker
Conditional jumping can be denoted with IF- conditional statement. If jumping condition is satisfied, jump.
Jumping aim must be program segment with marker. The program segment must lie in this program.
Conditional jumping instruction must occupy an undependent program segment.
There are several Conditional jumping instructions in one program segment.
IF condition GOTOF Lable ; Forwards jumping
IF condition GOTOB Lable ; Backwards jumping
| AWL | Illustration |
| GOTOF | Forwards jumping |
| GOTOB | Backwards jumping |
| Lable | Selected marker |
| IF | Conditional lay in symbol for jumping |
| Condition | Counting parameter as condition, computation expression |
| Operator | Meaning |
| = = | Equal to |
| <> | Unequal |
| > | Greater than |
| < | Smaller than |
| > = | Greater than or equal to |
| < = | Smaller than or equal to |
These comparison operations denote jumping condition. Computation expression can be used for comparison operation.
There are two outcomes of comparison operation: one is "satisfaction", the other is "dissatisfaction". When it is "dissatisfaction", the end value of operation is 0.
R1>1 ;R1 greater than 1
1<R1 ;1 smaller than R1
R1 < R2+R3 ; R1 smaller than R2 adding R3
R6 > =SIN(R7*R7) ; R6 greater than or equal to SIN(R7)2
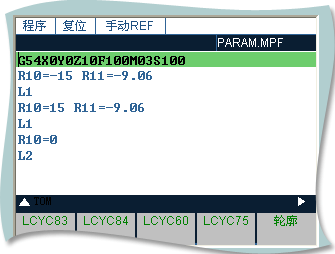
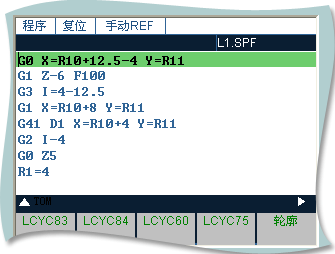
L1( semisphere ):
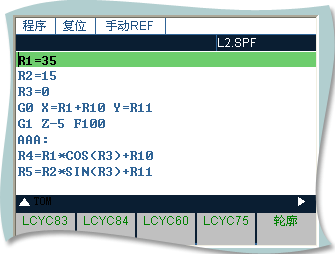
L2( ellipse ):
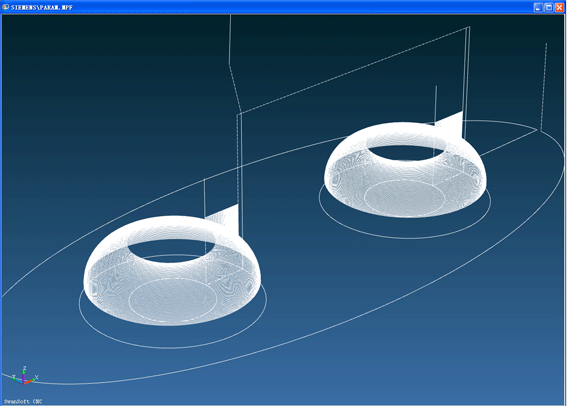
Effect drawing :
G54X0Y0Z10F100M03S100
R10=-15 R11=-9.06
L1
R10=15 R11=-9.06
L1
R10=0
L2
G0 X=R10+12.5-4 Y=R11
G1 Z-6 F100
G3 I=4-12.5
G1 X=R10+8 Y=R11
G41 D1 X=R10+4 Y=R11
G2 I-4
G0 Z5
R1=4
R2=90
AAA:
R3=R1*COS(R2)+4+R10
R4=R1*SIN(R2)-R1
G0 X=R3 Y=R11
G1 Z=R4 F300
G2 I=R10-R3
G0 Z1
R2=R2-1
IF R2>=0 GOTOB AAA
G0 Z10
M17
R1=35
R2=15
R3=0
G0 X=R1+R10 Y=R11
G1 Z-5 F100
AAA:
R4=R1*COS(R3)+R10
R5=R2*SIN(R3)+R11
G1 X=R4 Y=R5 F100
R3=R3+1
IF R3<=360 GOTOB AAA
G0 Z5
M17
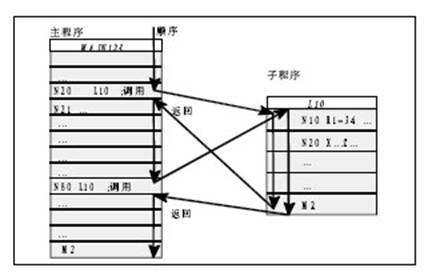
In principle there is no difference between main program and subprogram
Use subprogram to program often repeated machining, such as a certain figure. One form that subprogram is in main program is machining cycle including generally universal working procedure such as thread cutting. Many concrete machining is realized through specified counting parameter assigning.
The structure of subprogram is the same with main program's, and subprogram is stopped by M 2 in the last segment. main program return after subprogram end.
You can end subprogram by using RET besides M2.
When use RET to end subprogram or return main program G64 continuous path mode is not interrupted, while using M2 will interrupt G64 and come into halt state.
To select a subprogram expediently, you must give a name to the subprogram. Program name can be choosed freely but accord with:
- Initial two symbols must be letters
- Other symbols are letters, number or underline
- At best 8 symbols
- No separator
The means is the same with program name choosing in main program.
You can use program name to call subprogram in one program(main program or sunprogram). subprogram calling must occupy an undependent program segment.
Example :
N 10 L 785 P3 ; call subprogram L785
N20 WELLE7 ; call subprogram WELLE7
If you want to continuously run a subprogram time and time, you must write calling times in address P after program name of called subprogram, and the maximum times is 9999(P1...P9999) .
Example :
N 10 L 785 P3 ; call L785 ,run 3 times
Subprogram can be called not only in main program but also in other programs, and the procedure is called subprogram nesting. Subprogram nesting depth can be three level, that is to say four grades program interface(including main program interface).
Notation: when you use machining cycle to process, please take the attention that machining cycle also belongs to four grades program interface.
Take attention to parameter R too, and please do not change counting parameter of lower lever program interface by using the used counting parameter in higher lever program interface .